Clang IR (CIR)
Clang IR (CIR) is a new IR for Clang. ClangIR (CIR) is built on top of MLIR and it's basically a mlir dialect for C/C++ based languages in Clang. It's representation level sits somewhere between Clang AST and LLVM IR.
ClangIR upstreaming RFC was accepted in Feb 2024, and we already started the upstreaming work. Development is still currently done in the incubator but shall move to upstream as soon as the bulk of the base work lands.
Other resources:
- Oct 2023: Evolution of ClangIR: A Year of Progress, Challenges, and Future Plans. US LLVM Developers Meeting. video, pdf.
- June 2022: RFC: An MLIR based Clang IR (CIR)
Motivation
In a gist, an IR that can cover C/C++ higher level semantics enables a class of idiomatic diagnostics and performance optimizations that could be currently hard to explore on Clang AST or LLVM IR level.
By using MLIR, ClangIR leverages on a compiler framework to write passes, IR and quickly iterate design, while re-using community provided analysis and transformations that can be easily adapted for CIR.
What's ClangIR in practice?
ClangIR is a MLIR dialect that is also bound to Clang, meaning it lives inside the clang project and not as a mlir in-tree dialect. Some CIR operations optionally contain backreferences to the Clang AST, enabling analysis and transformation passes to optionally use AST information, while also allowing progressive lowering through late use of AST nodes.
By passing -fclangir to the clang driver, the compilation pipeline is modified and CIR gets emitted from ClangAST and then lowered to LLVM IR, backend, etc. Since our LLVM emission support is WIP, functionality is currently limited. To get CIR printed out of a compiler invocation, the flag -emit-cir can be used, which will force the compiler to stop right after CIR is produced. The picture below depicts how the compiler pipeline works:
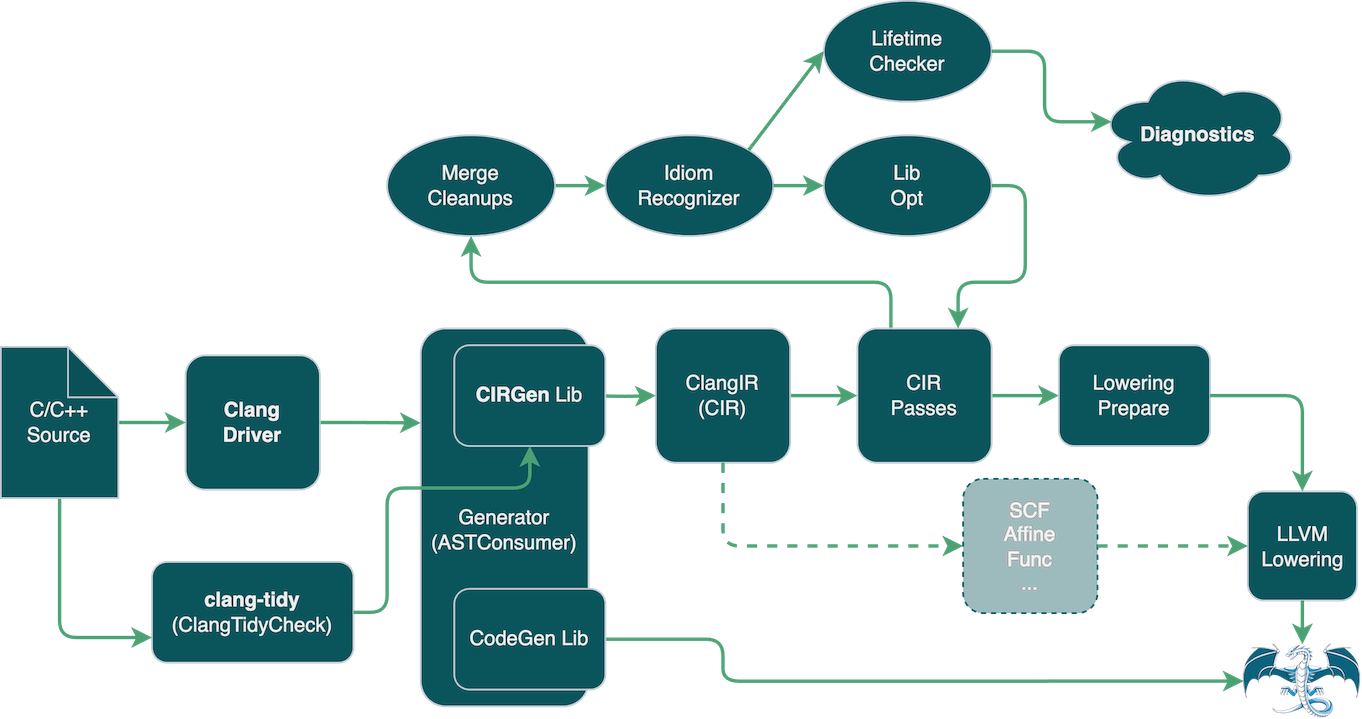
See instructions on how to build clang with ClangIR support and checkout some examples.
Current status
The project is active, here's a list of the current supported pieces:
-
CIRGen: the process of generating CIR out of the Clang AST. We support a good set of functionality from C/C++, but there are many missing. The CIR/CodeGen test directory is a good proxy of the current supported features.
-
LLVM lowering: generating LLVM IR out of CIR. About 50% of all programs in
llvm-testsuite/SingleSourcepass correctness checks. -
MLIR in-tree dialect lowering: basically CIR -> MLIR dialects, initial support to memref and some other dialects but currently not as active as LLVM lowering.
-
Lifetime checker: implementation of a C++ lifetime checker (for catching C++ dangling pointers) based in C++ lifetime safety paper. Currently handles pointer/owner/aggregate type categories, lambda dangling references via captures and can also catch idiomatic cases of dangling references in coroutines
coawaitexpressions.
Where to go from here?
Check out our docs for contributing to the project and get a tour in the CIR Dialect.
Inspiration
ClangIR is inspired in the success of other languages that greatly benefit from a middle-level IR, such as Swift and Rust. Particularly, optionally attaching AST nodes to CIR operations is inspired by SIL references to AST nodes in Swift.
Github project
This project is part of the LLVM incubator, the source of truth for CIR is found at https://github.com/llvm/clangir.
The main branch contains a stack of commits, occasionally rebased on top of LLVM upstream, tracked in base branch.
Last updated: Tue May 14 16:52:35 PDT 2024